|
||
| Research Projects | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Design & Synthesis of Novel Glycopeptides
with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity against VRE & VRSA |
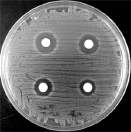
Vancomycin is the drug of last resort against multi-resistant bacteria, such as MRSA. The emergence of vancomycin-resistant bacteria (VRE, 1986-; VRSA, 2002-) is a serious concern in clinics.
Our efforts in this area culminated to the development of a vancomycin polymers (Chem. Commun. 1999, 1361), dimers (Chem. Commun. 2007, 251-253; with an in vivo activity), and monomer derivatives (Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 960; J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2528) with enhanced activity against VRE. We recently reported the first synthesis of the VRE/VRSA's depsi-lipid I, a precursor of bacterial cell wall, which can be used for the detailed mode of action analysis (Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 12104). |
|
||||||||||||||
| Synthetic Studies of Biologically Active Natural Products | Some of our targets are....
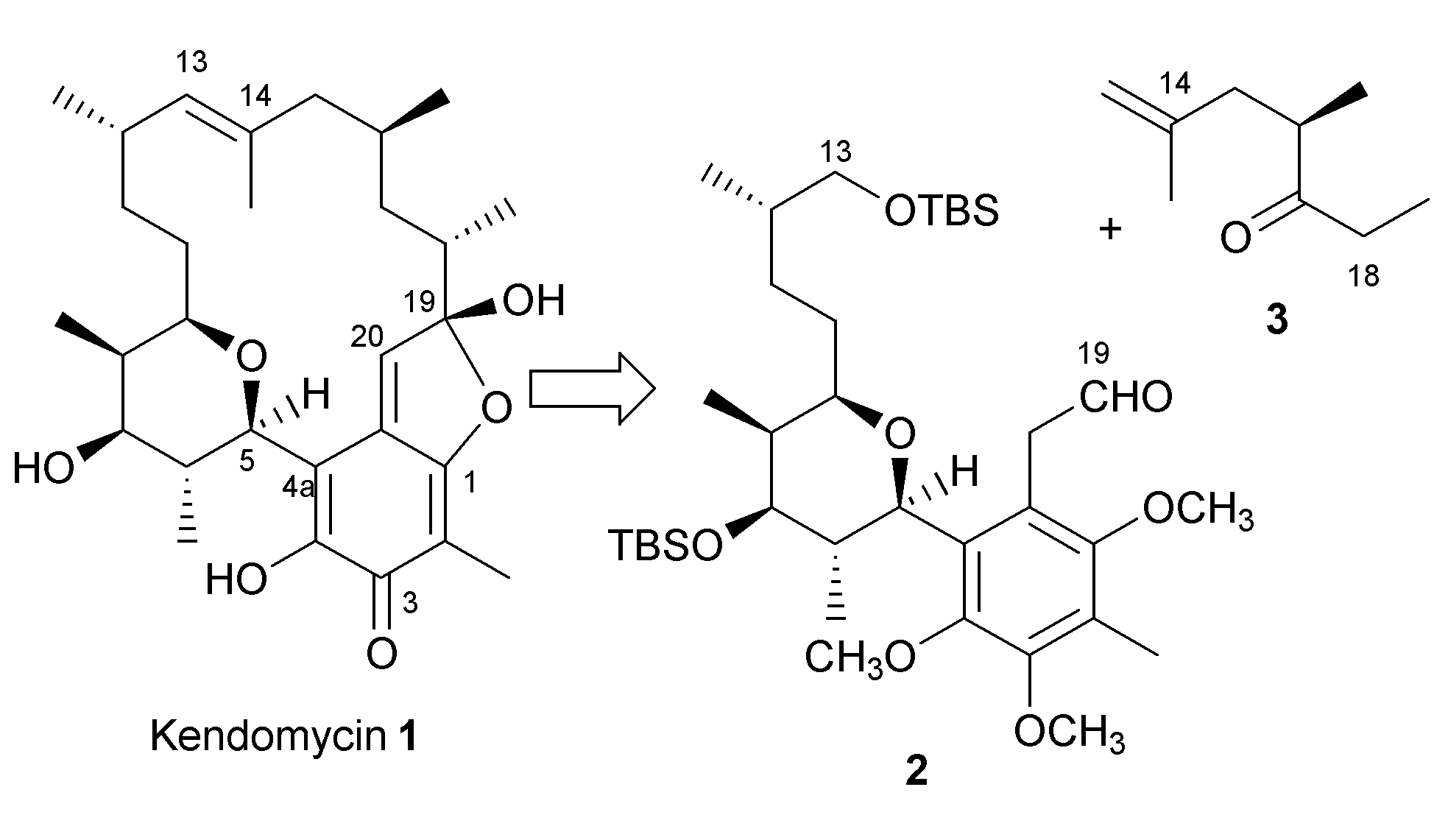
Kendomycin is the relatively new antibiotics with macrocyclic carbon-ring (Takeda Chemical Industry, Japan). A researcher in UK reported its activity against a vancomycin-resistant S. aureus(GISA, Mu50). Our long standing interests on vancomycin-resistance prompted us to initiate synthetic efforts. (Sengoku, Arimoto, Uemura, Chem. Commun., 2004, 1220; Chem. Lett. 2007, 726-728)
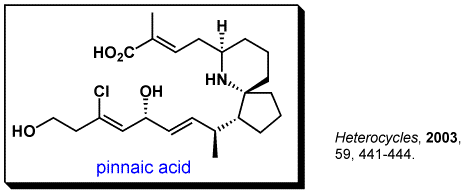
These compounds were isolated by Prof. Uemura (presently at Kanagawa University). More than 15 research groups are currently involved the synthesis of these compounds.
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Paralytic substances in the venom of spider wasp |
The solitary spider wasp Cyphononyx dorsalis is well known to hunt spiders: it uses its stinger to paralyze its prey to feed its larva. This wasp venom was fractionated by bioassay-guided chromatography and so far three proteins were identified. The recombinant arginine kinase-like protein exhibited paralytic activity against spiders. (Insect Biochem. Mo. Biol. 2007, 278-286.) |
 |
||||||||||||||
| Solution structure of marine natural products |
Natural toxins with high specificity to their molecular targets have been contributing greatly for chemical biology of ion channels. A huge natural product palytoxin [mw 2680, LD50 value of 15-450 ng/kg against mice], is a typical example, and has an entirely unique function to convert Na/K pump into a non specific ion channel. We have investigated a solution structure of palytoxin using SAXS, and found that it formed an associated dimer of 5 nm length in aqueous solution. (with Profs. Fujisawa and Uemura; Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 897-899, and inside front cover of OBC, 2007, issue 6) |
 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
||